Development and Assessment of a New Single-Use Tool for Joining Ti-6Al-4V by FSW
By Jonathan Martin
Industrial Need
Friction Stir Welding is now a well-established process for joining light alloys. The relatively low temperature (~500°C) required to soften and plasticise aluminium alloys allows the use of steel based FSW tools, a material which is readily available, low-cost and has a good welding life. However, tool materials and designs for welding higher temperature alloys such as titanium present a significant challenge. Tool materials must not only be able to withstand the high welding forces and torque levels, but must also operate at high temperatures (typically 1000-1200°C). Currently refractory metals, such as tungsten and molybdenum are the preferred tool materials but there is only very limited reported use by industry. These materials have provided a FSW tool with properties capable of making welds; however, the cost of the material, producing the tool features and weld life puts a very large burden on the commercial viability of FSW in all but very high value applications. TWI has undertaken feasibility welding trials to assess the potential suitability of using a monolithic silicon nitride tool. During this work, silicon nitride demonstrated its potential suitability as it exhibited no deformation and its cost is an order of magnitude less than refractory metals. This report describes initial trials with the objective of developing a low-cost, single-use, tooling system based on silicon nitride for welding titanium alloys. A lower cost tooling system could make FSW more financially accessible to industries other than aerospace, where the product would benefit from the high quality welds produced by friction stir but could not justify the cost of the current FSW tooling systems.
Key findings
- A tooling system has been developed capable of making 3mm deep, 2m long bead-on-plate (BoP) welds, in Ti-6Al-4V, using single-use ceramic inserts costing less than 50 euros.
- The BoP welds have good static weld properties and visual appearance.
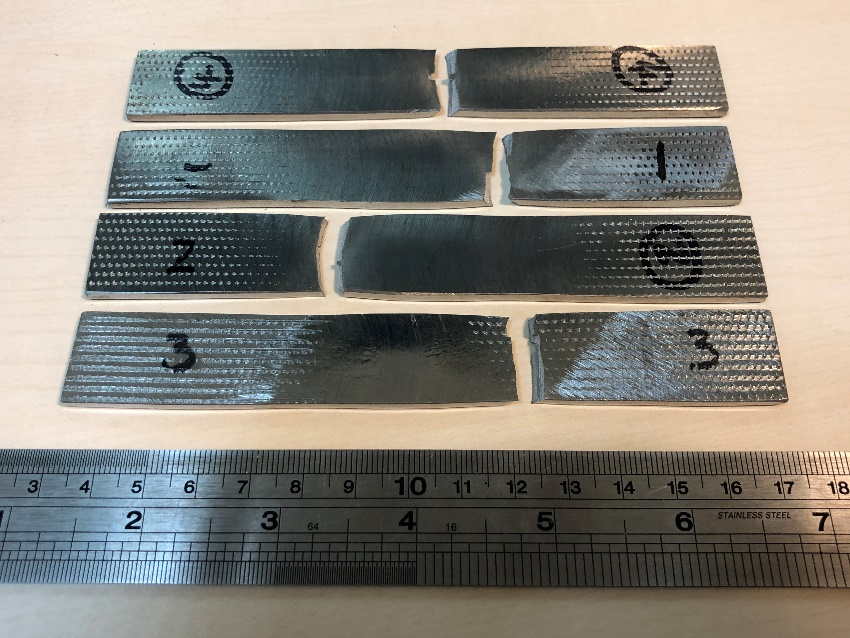
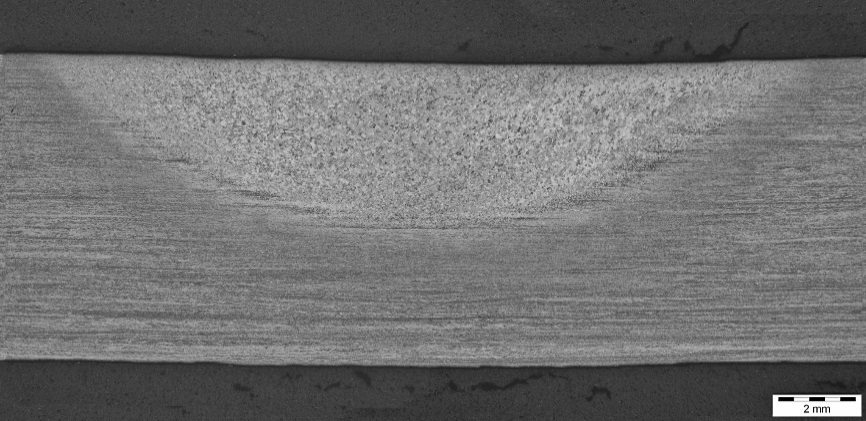
Macrograph from the centre of a 2m long bead-on-plate friction stir weld in Ti-6Al-4V made using the new ceramic insert tool.
Failed tensile specimens showing failure of the welded specimens in the parent material:
Top to bottom: (4) Parent material with no weld; (1) Weld start; (2) Mid-weld; and (3) Weld end.
