Development and Demonstration of Data Analytics and Machine Learning for Engineering Applications
TWI Industrial Member Report 1193-2024 [pdf / 2,310KB]
By Madie AllenPhD, AWeldI
Imran Bhamji and
Jeremy Morgan
Industrial Need
It is becoming increasingly important for TWI and Industrial Members to demonstrate their capabilities in data based technologies, such as data analysis and machine learning (ML), and to understand the benefits these technologies can provide, as we embrace Industry 4.0 and move through into industry 5.0. Digitalisation and automation are key factors in the future of industry and it is import TWI establish themselves as, not only competent but, leaders in this field.
The project was designed to explore various technologies, relevant to the engineering industry, and investigate how these can be implemented within TWI as well as providing insight on best practice for those Industrial Members looking to implement similar systems within their own organisations.
Key Findings
- The applicability of data-driven analysis and machine learning methods to engineering applications has been investigated and demonstrated through two use cases.
- NLP techniques were used to demonstrate the generation of keywords from Weldasearch abstracts. Good results were achieved, albeit on a limited data set.
- An efficient automation process, for image processing, was developed which predicted percentage porosity to within 0.01% variance of manual porosity calculation.
- Machine learning methods were used to demonstrate how these can be beneficial in uncovering relationships between process parameters and porosity for additive manufacturing methods.
- The importance of security concerns for open source software, IP protection for historical project data, and historical inconsistency in data recording and storage was highlighted.
Impact
Within this project, TWI have demonstrated their capabilities in a variety of automation and machine learning processes. The project has also shown how these techniques can be implemented within engineering applications to achieve quality results. Furthermore, as a result of this work, TWI is able to guide industrial members, interested in these methods, towards suitable approaches as well as highlighting any potential challenges they may come across.
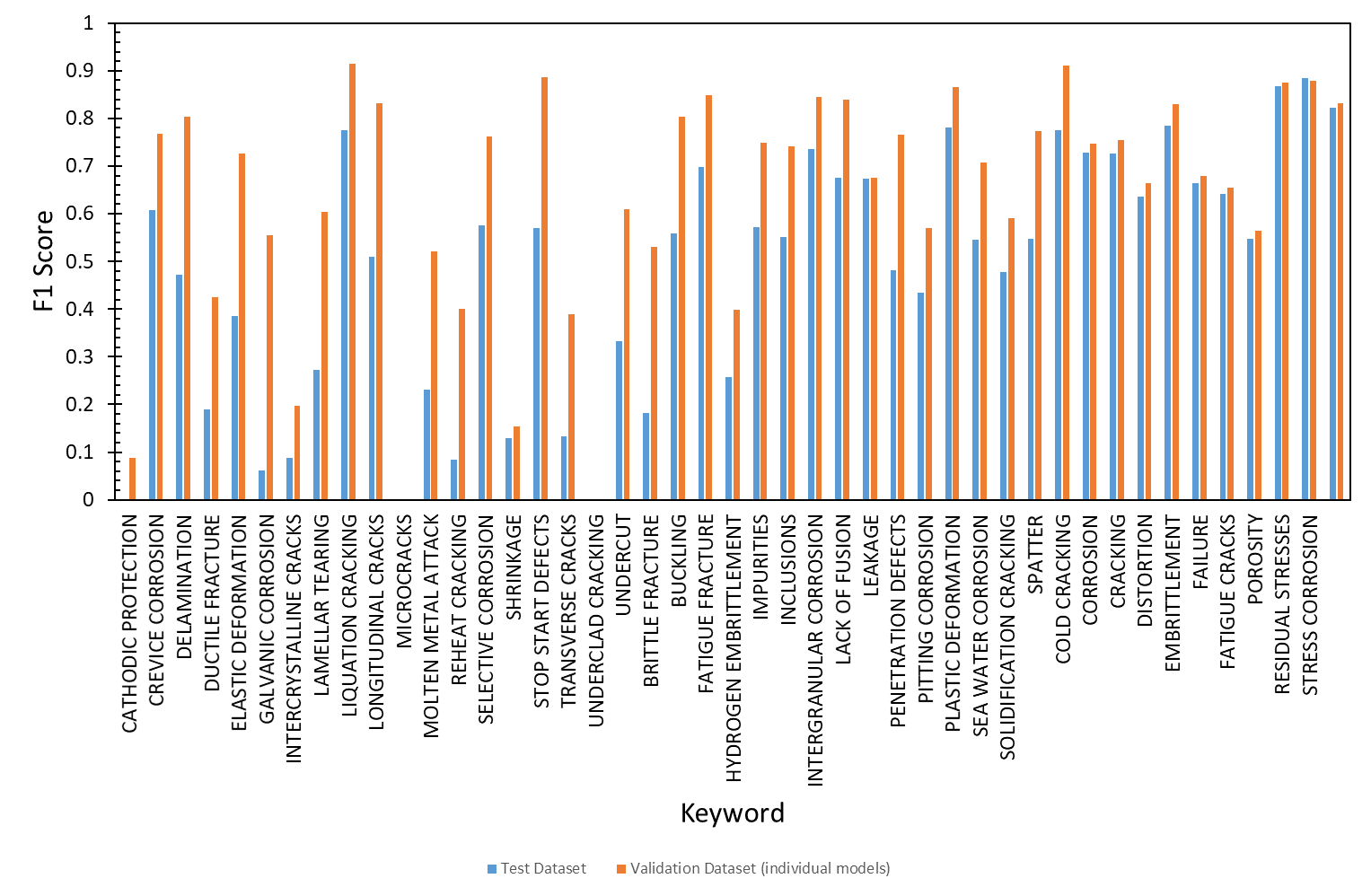
Accuracy of natural language processing (NLP) model.
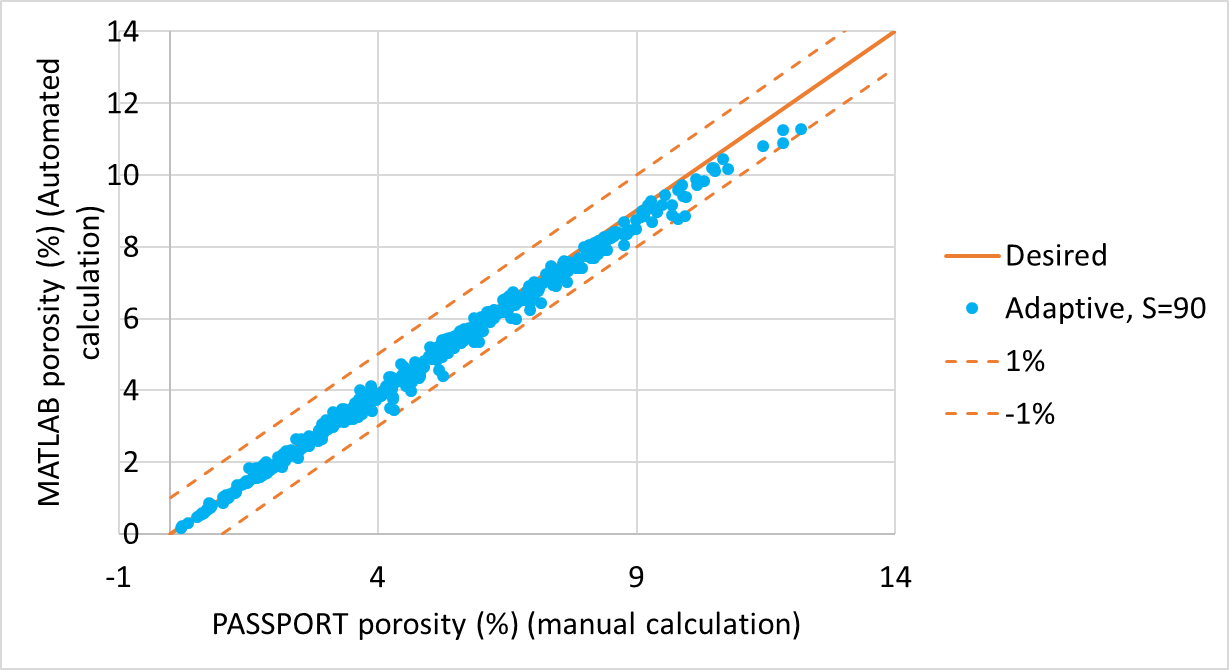
Comparison of automated image processing porosity calculations against manually calculated values.
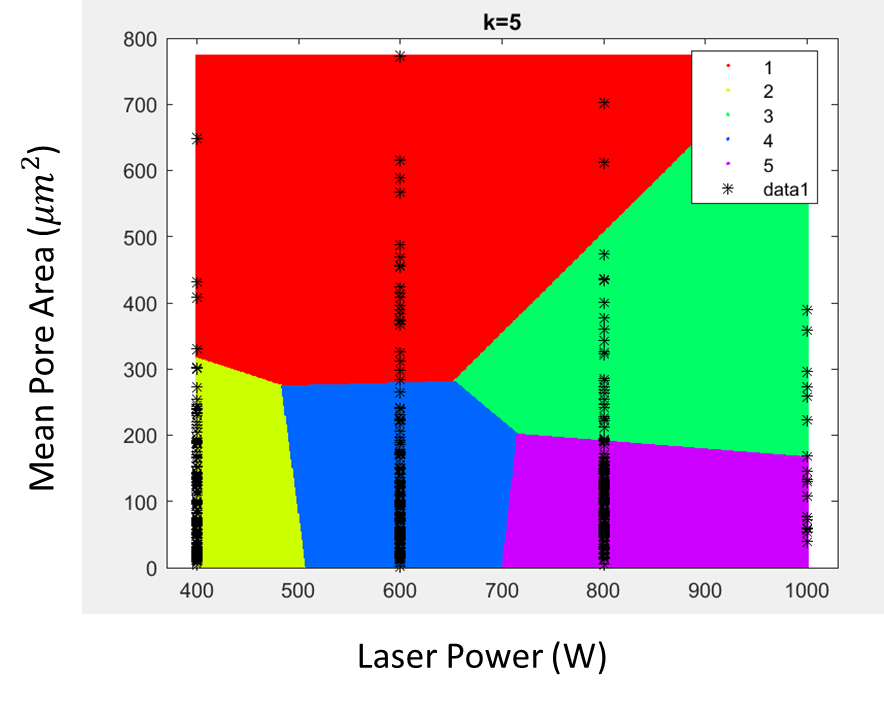
Example of the use of clustering to explore relationships between process parameters and porosity.