Thu, 06 March, 2025
The shift towards renewable energy is a global priority, and innovative research plays a crucial role in driving this transition. In a significant step toward sustainable power generation, Mehran Izadkhah, in collaboration with Universiti Sains Malaysia (USM) and TNB Labs, successfully presented their technical paper, “Utilizing Biomass for Sustainable Energy: A Focus on Power Plants in Malaysia,” at the International Conference on Energy, Power, Environment, Control, and Computing. The event, hosted by University of Gujrat and GIFT University, took place on February 20th and brought together leading researchers, industry experts, and policymakers to discuss advancements in energy efficiency, environmental sustainability, and emerging power technologies.
Understanding the Research: Biomass as a Sustainable Energy Source
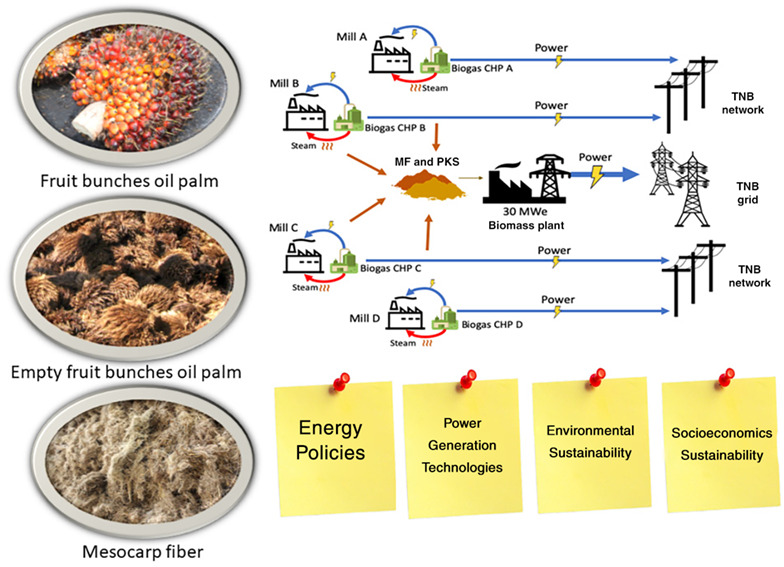
The technical paper delves into the potential of biomass as a renewable energy source, particularly for power plants in Malaysia. Currently, fossil fuels such as coal, natural gas, and oil dominate Malaysia’s energy mix, contributing to high carbon emissions and environmental degradation. The paper highlights biomass—derived from agricultural residues such as palm oil waste, rice husks, and wood pellets—as a viable alternative to conventional fuels.
The research specifically addresses biomass co-firing, a process where biomass is blended with coal in power plants. This method allows for:
- Reduction in greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions while maintaining energy output.
- Improved energy efficiency through higher boiler performance.
- Utilization of locally available resources, reducing dependence on imported fuels.
- Compliance with sustainability goals, such as Malaysia’s National Biomass Strategy 2020, which aims to integrate more renewable sources into the energy sector.
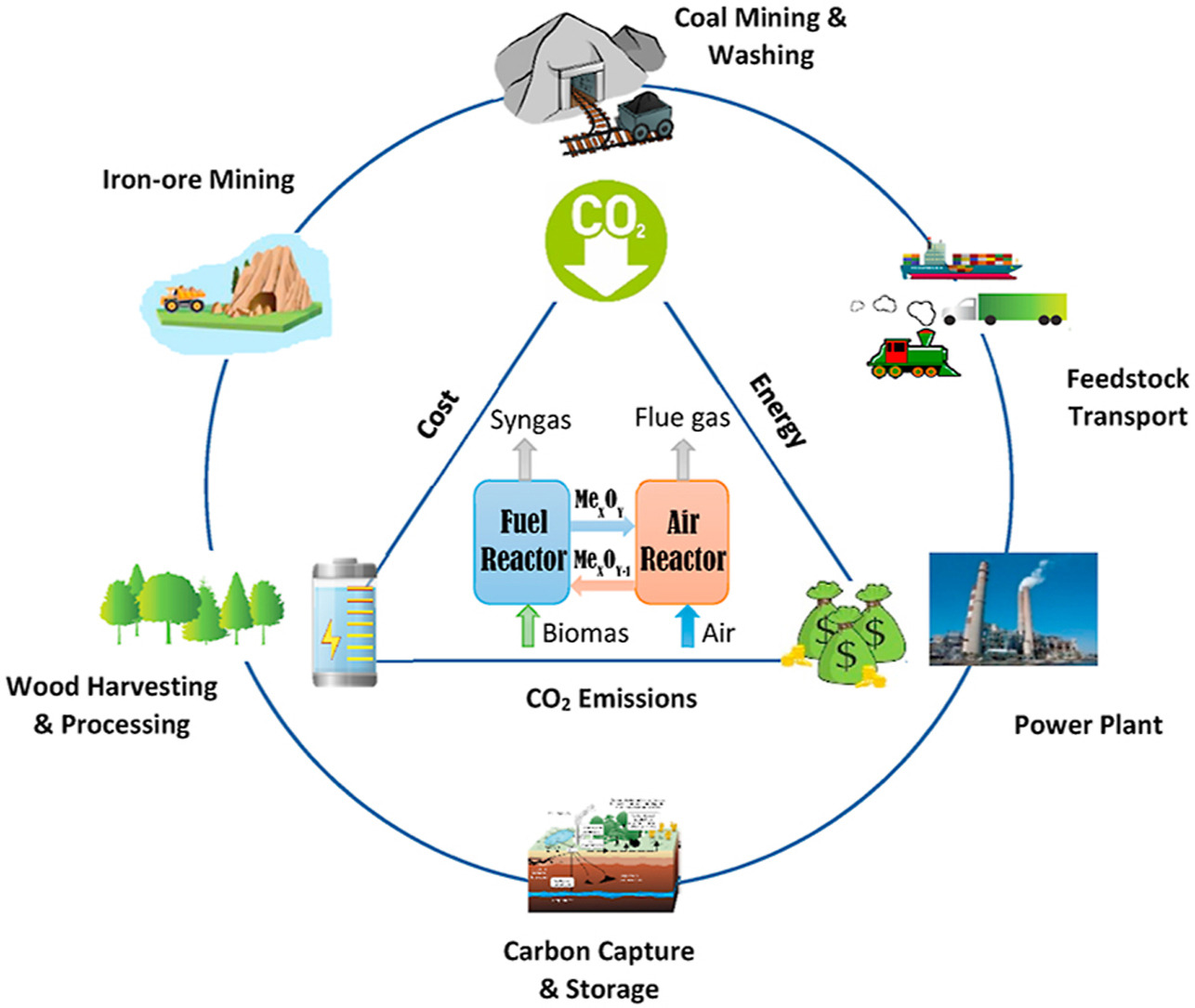
Challenges and Technical Considerations
While biomass presents numerous advantages, its large-scale adoption comes with operational challenges. The paper explores key issues such as:
- Boiler Integrity and Durability: Biomass combustion can lead to increased corrosion, slagging, and fouling in boiler tubes, affecting plant efficiency.
- Energy Density Variations: Biomass generally has a lower energy content than coal, requiring modifications in combustion processes.
- Supply Chain Constraints: The logistics of sourcing, storing, and transporting biomass fuel must be optimized for economic feasibility.
- Ash Deposition and Emissions Control: Managing ash-related damage in power plants is crucial for long-term operational success.
To address these concerns, a number of technical solutions and recommendations were addressed in this paper. These are as a result of the observations and outcomes of monitoring the rate of degradations mechanisms with and without adding biomass co-firing.

The Role of Government Policies and Industry Adoption
The study also emphasizes the importance of government initiatives in promoting biomass adoption. Policies such as Malaysia’s Renewable Energy Policy and Action Plan encourage industries to integrate biomass as a key component of their energy strategy. Leading energy providers, such as TNB Labs and Kapar Energy Ventures, are already conducting pilot projects to assess the feasibility of biomass co-firing. These initiatives demonstrate growing industry interest in transitioning toward cleaner energy alternatives.
Conclusion: Driving a Sustainable Energy Future
The successful presentation of “Utilizing Biomass for Sustainable Energy” marks an important step in advancing the discourse on renewable energy adoption in Malaysia and beyond. By identifying both opportunities and challenges in biomass utilization, this research provides practical insights for industry leaders, researchers, and policymakers. The findings contribute to a broader goal of reducing carbon footprints, enhancing energy efficiency, and ensuring long-term sustainability in power generation.
With experts like Mehran Izadkhah and his team leading the way, the transition toward cleaner and more efficient energy solutions is becoming increasingly attainable. As industries explore innovative approaches to renewable energy, biomass stands out as a key player in shaping a greener and more resilient future.

About Mehran:
Regional Engineering Manager
“Mehran joined TWI in 2009. He has managed several projects of risk-based inspection, damage mechanism identification, fitness-for-services, offshore structural integrity assessment, pipeline integrity assessment, corrosion control, cathodic protection, protective coatings, and failure investigations.
He led the development of fully quantitative and semi-quantitative procedures, methodologies, and algorithms utilized in RBI assessment for various assets such as pipelines, boilers and fixed equipment. He is now the Product Manager for TWI’s Risk-Based Inspection (RBI) software RiskWISE®, leading and managing the developments of TWI’s RBI and Integrity management software. Mehran is currently pursuing his MPhil at Universiti Sains Malaysia (USM), focusing on boiler integrity and development of predictive models for boiler tube failures, under funding from TWI
To learn more please contact: Mehran.Izadkhah@twisea.com